Applications:
Powders having low aspect ratios, glass or plastic spheres, metal spheres, toners.
Available measures:
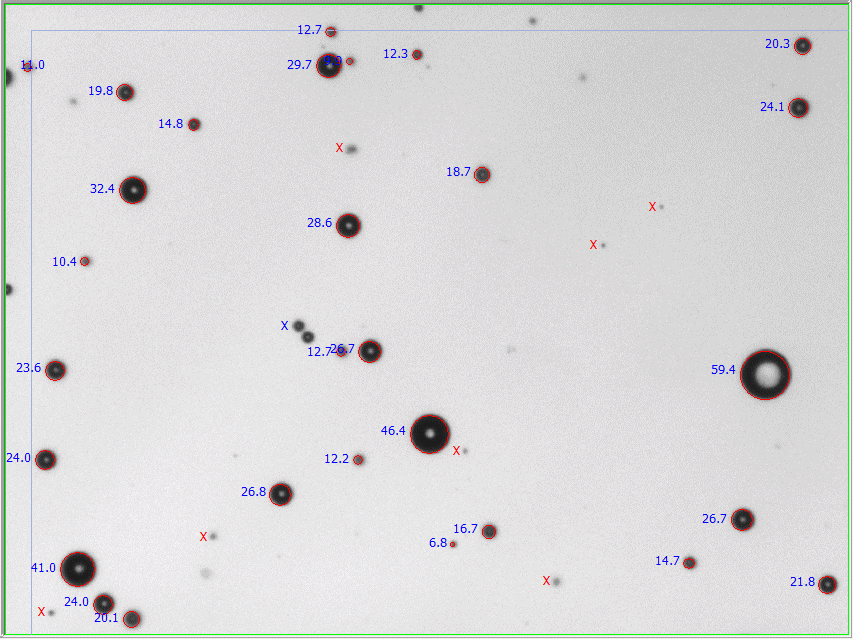
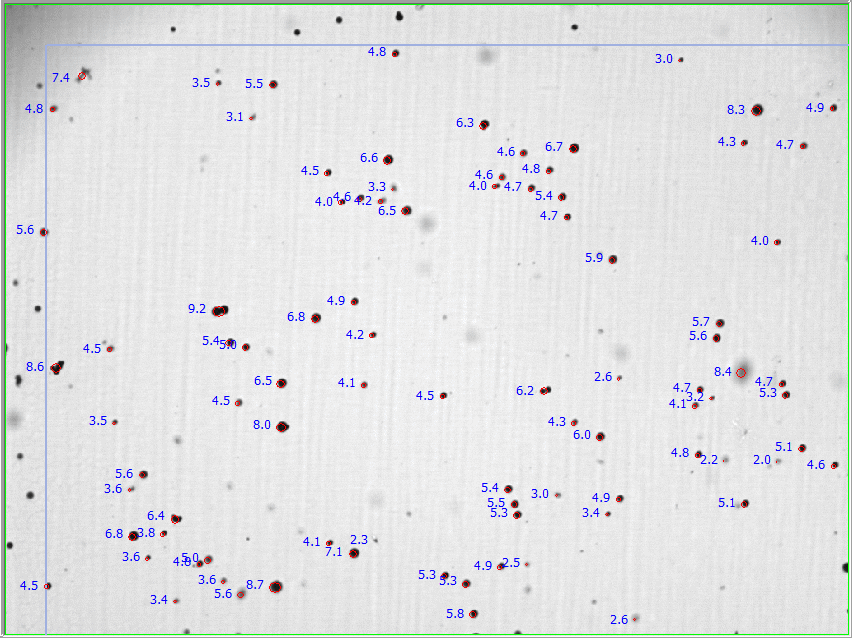
- Equivalent Circular Area diameter
- ECAD is the diameter of a circle having the same area as the original shape.
- Equivalent Circular Perimeter diameter
- ECPD is the diameter of a circle having the same perimeter as the original shape.
- Bounding Circle diameter
- BCD is the diameter of the smallest circle that completely encloses the shape.
- Mean Radius diameter
- MRD = 2 times the average radius of 48 radii measured at equal angular intervals. Usually very close to ECAD.
- Circularity
- Circularity is a measure of “how circular” the shape is, and by inference, how spherical the actual particle is. Area-based circularity is defined as 4A / (pi*D*D) where A is the shape’s area and D is the BCD diameter (see above). A perfect circle has a circularity of 1.0 and anything else has a circularity less than 1.0.
- Smoothness
- Smoothness is a measure of how smooth and regular the perimeter of the shape is. It is a number between 0 and 1, defined as (4*pi*A)/(P*P) (A = area, P = perimeter). Smoothness is affected by small fluctuations in the perimeter and also by larger “out-of-round” variations of the outline.
- Compactness
- Compactness is the square root of Circularity and does not vary as much as Circularity.
Images showing ECAD values
 |
 |
 |

