Understanding Fluid Contamination Monitoring & the new ISO 21018 standards.
The Role of Dynamic Image Analysis (DIA)
Contaminant monitoring in hydraulic fluids, fuels, and lubricants is essential for ensuring system performance and longevity. Traditional particle counting methods, guided by ISO 11171’s light obscuration technique, primarily focus on particle size and concentration but lack the ability to identify contamination sources or provide detailed particle shape analysis. Without this added information, experts are needed to make educated guesses as to what the source of contamination in measured oil is. In addition, many of these light obscuration techniques are not field based requiring time to get data resulting in machine downtime or worse…. operating a machine that is out of spec.
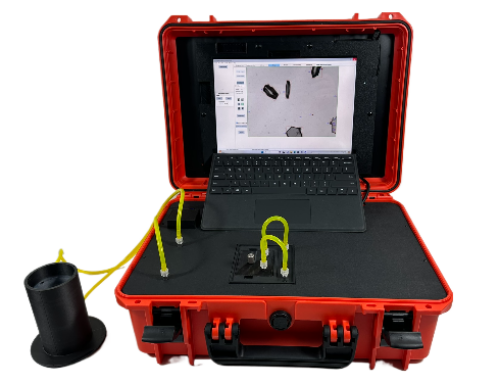
Dynamic Image Analysis (DIA) introduces a more comprehensive approach to fluid contamination assessment by capturing detailed images of particles, allowing for differentiation between contaminants such as wear debris, fibers, water droplets, and air bubbles. This capability enhances contamination monitoring by offering better insights into particle characteristics and potential sources. No educated guessing as to the source of the contamination. Real-time and field-based results with thumbnail images reduce the need for an expert to find the accurate source of any problem.
The Industry’s New Standard: ISO 21018-1
Historically, contamination monitoring relied on methods conforming to ISO 11171, which is primarily designed for light obscuration techniques. However, the industry has acknowledged the need for alternative monitoring technologies, leading to the introduction of ISO 21018-1:2024.
This standard accommodates techniques beyond light extinction, including Dynamic Image Analysis, providing a validated framework for fluid contamination assessment in hydraulic systems, fuels, and lubricants. In addition, this new standard was created because although there are good reasons to have alternative techniques for fluid contamination, some of these complimentary techniques can’t be calibrated according to the ISO 11171. Although other techniques are discussed, here we will focus on Dynamic Image Analysis and how this technique can benefit this market.

Advantages of Dynamic Image Analysis
✅ Detailed Contaminant Identification – Captures high-resolution images of particles, helping distinguish different types of contaminants. with particle sizes down to 2 microns in size.
✅ Real-Time Monitoring – Enables on-site, rapid decision-making by providing instant contamination data. No expert needed to identify source of contamination. System is portable and battery operated.
✅ Proactive Maintenance – Helps industries trace contamination sources, prevent system failures, and optimize maintenance efforts.
✅ ISO 21018-1 Compliance – Recognized as an alternative contamination monitoring technique, making it a valuable method for fluid cleanliness assessment.
Comparing Contamination Monitoring Methods
| Feature | Dynamic Image Analysis (ISO 21018-1) | Light Obscuration (ISO 11171) |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Detection | 2 µm to 300+ µm | 4 µm to ~100 µm |
| Shape Analysis | Yes | No |
| Thumbnail Images | Yes | No |
| Contaminant Source ID | Yes | No |
| On-Site Analysis | Yes | Limited |
| Compliance | ISO 21018-1 | ISO 11171 |
| Shape Classification | Yes | No |
Applications of Dynamic Image Analysis in Fluid Contamination Monitoring
🚛 Fuel and Lubrication Monitoring – Ensures compliance with cleanliness standards and detects contamination in real-time.
🏭 Industrial & Manufacturing Equipment – Reduces wear-related failures with proactive contamination tracking.
🛢 Hydraulic Systems – Improves fluid cleanliness and enhances equipment reliability with precise contaminant identification.
🔬 Research & Laboratory Applications – Supports contamination studies with detailed particle characterization.
Advancing Fluid Contamination Monitoring
Dynamic Image Analysis represents a significant advancement in contamination monitoring by providing in-depth particle characterization beyond simple particle counting. By aligning with ISO 21018-1, this technique enables industries to improve contamination assessment, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance system reliability.
🚀 Explore how Dynamic Image Analysis is shaping the future of fluid cleanliness monitoring.
📩 For more details, visit www.ParticleShape.com to learn more.
Other articles to view….
View our Blog post on Particulates in Fuel and Lubricating Oils here.